Bioelectronics Medicine and Electroceuticals
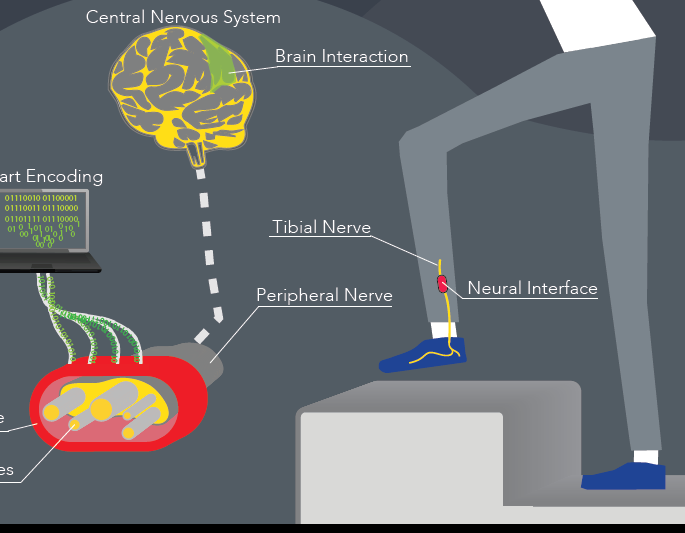
Diabetic patients with peripheral neuropathy (DPN) cannot perceive foot sole and thus harmful conditions (e.g. a rock in the shoe) for the foot, facing wounds that eventually turn into ulcer, which at its turn leads to amputation. Together with diabetes, also the prevalence and incidence of a painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy is increasing each year. The presence of this pain leads to substantial interference in sleep, enjoyment of life and quality of life, normal work, mobility, social activities and mood. Sometimes it provokes necessity for devices for mobility restoration. Neuropathic pain is due to damages to the nervous system. The aim of the project is to develop the first neuroprosthesis restoring close-to-natural foot sensations, through electrical nerve stimulation, to patients with diabetic neuropathy. This framework would have potential multiple uses: for the restoration of leg functions after diabetic neuropathy occurrence and for neuropathic pain suppression. We will achieve it starting from detailed computational models, passing through device implementation and final validation with humans.
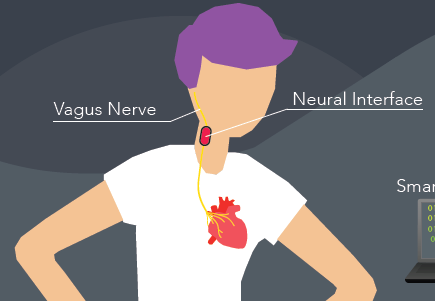
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is one among the most fascinating possibilities in the field of neuroengineering. It is the longest nerve of the autonomic nervous system in the human body, and the optimal target for a neuroengineering intervention. It is connected with parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. Yet lot about its function and topographic structure is unknown. Several applications are currently using VNS to treat epilepsy and treatment-resistant major depressive disorder, among several other applications, which are undergoing tests. The goal of our project is to construct a mechanical and electrical models of VNS, based on the animal data, and to exploit it for better understanding of underlying mechanisms, together with the design of optimal interface.
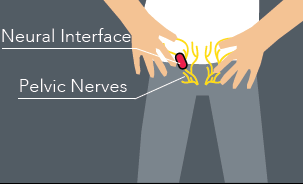
The amount of patients suffering from erectile dysfunctions (ED) is huge, and is rising worldwide. The global scope of our this project is the development of a subcutaneously implantable bidirectional stimulation system to restore erectile functions in patients with any type of diabetic, neuropathic or neurovascular disorder affecting vessels, hormones the brain, spinal cord, cavernous and pudendal nerves. Compared to the existing therapies (pharmaceutical therapies, penile implants, LI-ESWT, Vacuum erection devices, impulse magnetic field therapy, etc.) we want to develop the first method to restore a full erection, together with the natural sensation feedback. Animal studies showed that the cavernous nerve stimulation could potentially induce complete erection in subjects suffering from erectile dysfunction. We will develop the computational model, which will guide the design of an optimal neural interface and its modality of use. Then it will be tested in animal model, and finally validated in humans.