Diabetic Neuropathy
The Neuroengineering Lab is recruiting participants for several research studies for clinical applications. Please contact us if you are interested to participate and fit the inclusion criteria for any of the studies listed below!
Enhancing functional performances in people with peripheral neuropathy through the restoration of sensory feedback – NeuroLegs
Diabetic patients could suffer from symmetrical polyneuropathy (DSPN), which is a common complication caused by prolonged glucose unbalanced levels that lead to nerve damage. DSPN is the most common neuropathy in diabetics and currently affects 1.7% of the world population (Abbott et al., 2011). The symptoms of DSPN are several, but one of the most common and debilitating is the loss of sensations from the extremities (Archer et al., 1983).
Our goal is to enhance functional abilities in diabetic subjects with neuropathy through the restoration of sensory feedback. The sensory feedback will be provided through superficial electrical stimulation, which is non-invasive and not painful. We will explore if the regained sensations will allow better walking abilities, improve balance and reduce the risk of falling. This project is founded by the Neuroengineering Laboratory of ETH.
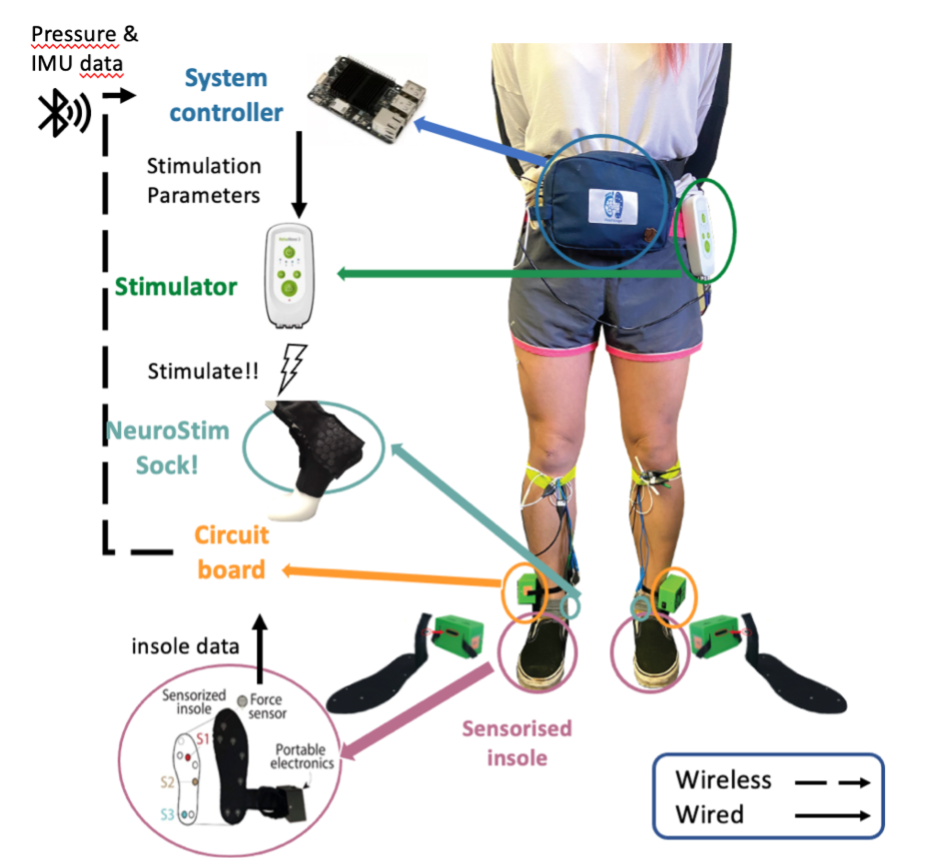

NeuroLegs
Inclusion criteria
- Diabetic neuropathy
- The subject should be in the range of 18-80 years old
- Loss of sensations from the extremities
- The subject should be able to comfortably walk, sit and stand
If any of the inclusion criteria are ticked ‘no’ then you will not be eligible for the study
Exclusion criteria
- Cognitive impairment
- Severe comorbidities
- Untreatable ulcers
- Pregnancy
- Prior or current psychological diseases such as borderline, schizophrenia, depression or maniac depression
- Acquired brain injury with residual impairment
- Excessive sensitivity or pain to electrical stimulation with surface electrodes
Contact Information
Lauren Chee, PhD Student,
Prof. Dr. Stanisa Raspopovic, Assistant Professor,
Ethical Approval Number: EK 2019-N-97